路由器作为家庭及企业网络的核心枢纽,其适配网络的能力直接影响数据传输效率、覆盖范围和用户体验。适配网络的本质是通过硬件性能、软件算法、频段分配、信号调控等多维度的协同优化,实现网络资源与终端需求的精准匹配。现代路由器需兼顾多平台兼容性(如PC、手机、IoT设备)、多协议支持(Wi-Fi 6/5G/IPv6)、多场景适应(高密度环境/大户型/户外),同时解决信号干扰、带宽分配、安全防护等痛点。适配过程涉及频段选择、信道优化、功率调节、MU-MIMO技术应用、QoS策略配置、固件迭代等多个层面,需结合物理环境、用户习惯、设备类型动态调整。例如,在设备密集场景中,需启用160MHz频宽和智能信道切换;而在长距离覆盖场景中,则需采用低信噪比模式和Mesh组网技术。此外,路由器还需适配不同运营商的网络架构(如桥接模式/PPPoE拨号),并针对游戏、直播等高优先级流量进行带宽保障。

一、频段选择与动态切换
频段适配策略
路由器需根据终端类型、传输距离和干扰情况选择2.4GHz或5GHz频段。2.4GHz穿透性强但速率低,适合远距离覆盖;5GHz速率高但穿透弱,适合短距离高速传输。双频合一技术可自动为设备分配最优频段。
| 频段 | 优势 | 适用场景 | 典型速率 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.4GHz | 穿透力强、覆盖广 | 大户型基础覆盖、IoT设备 | 理论最高600Mbps |
| 5GHz | 干扰少、速率高 | 高清视频、在线游戏 | 理论最高2400Mbps |
| 6GHz(Wi-Fi 6E) | 超低延迟、独立信道 | 企业级高密度部署 | 理论最高9.6Gbps |
二、信道优化与抗干扰机制
信道动态分配
路由器需实时检测周边无线环境,通过CSI(信道状态信息)分析干扰源,自动切换至空闲信道。例如,在2.4GHz频段避开DSSS信道(如信道1、6、11),在5GHz频段启用80MHz或160MHz频宽以提升吞吐量。
| 信道宽度 | 可用信道数 | 适用场景 | 最大吞吐量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20MHz | 13(5GHz) | 高干扰环境 | 理论433Mbps |
| 40MHz | 9(5GHz) | 中低密度场景 | 理论867Mbps |
| 80/160MHz | 5(5GHz) | 低干扰高速需求 | 理论1733Mbps+ |
三、发射功率与覆盖平衡
功率动态调节
路由器需根据终端距离动态调整发射功率,避免近距离高功率浪费或远距离信号衰减。例如,通过RF信号强度反馈,对靠近的设备降低功率(如5dBm),对远端设备提升功率(如20dBm)。
| 功率等级 | 覆盖范围 | 适用场景 | 功耗表现 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 低功率(5-10dBm) | 10-15米 | 小型房间/低干扰环境 | 节能模式 |
| 中功率(15-20dBm) | 20-30米 | 常规家庭覆盖 | 均衡模式 |
| 高功率(25-30dBm) | 40-50米 | 大户型/穿墙需求 | 高耗电模式 |
四、设备兼容性与协议支持
多协议适配能力
路由器需兼容不同设备的网络协议,例如:为老旧设备支持802.11b/g/n,为新设备启用802.11ac/ax;针对IoT设备开启BLE/ZigBee网关功能;对企业用户支持IPv6过渡技术(如DHCPv6PD)。
| 协议类型 | 典型设备 | 适配要求 | 性能影响 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 802.11b/g/n | 早期手机/笔记本 | 强制20MHz信道 | 速率上限150Mbps |
| 802.11ac | 中高端手机/PC | 支持MU-MIMO | 理论1.3Gbps |
| 802.11ax(Wi-Fi 6) | 新款旗舰设备 | OFDMA+BSS着色 | 理论9.6Gbps |
五、安全策略与加密适配
加密方式动态匹配
路由器需根据设备能力和安全需求选择加密协议:对旧设备使用WPA2-PSK(AES),对新设备启用WPA3(SAE);针对IoT设备可采用轻量级加密(如TKIP)或独立VLAN隔离。
| 加密协议 | 安全性 | 兼容性 | 性能损耗 |
|---|---|---|---|
| WEP | 极差(已破解) | 仅2010前设备 | 无显著影响 |
| WPA2-PSK(AES) | 高(未被攻破) | 全平台支持 | 约5%吞吐量下降 |
| WPA3-SAE | 极高(抗暴力破解) | 新设备支持 | 约10%吞吐量下降 |
六、固件功能与模块化扩展
固件适配性升级
路由器需通过固件更新支持新兴功能,例如:OpenWRT系统可加载DD-WRT插件实现广告拦截、USB加速;企业级固件支持CAPWAP协议与AC控制器联动。模块化设计允许外接4G/5G模块或PoE交换机扩展功能。
| 固件类型 | 核心功能 | 适用场景 | 扩展性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 原厂封闭式固件 | 基础路由/防火墙 | 家庭用户 | 低(仅官方更新) |
| OpenWRT/LEDE | 自定义脚本/插件 | 技术爱好者 | 高(支持Python/Lua) |
| 企业级固件(如ArubaOS) | 集中管理/VPN隧道 | 企业网络 | 中(依赖厂商授权) |
七、QoS策略与流量优先级
带宽智能分配
路由器需识别应用层协议(如UDP游戏流、TCP视频流、HTTP网页),通过DPI(深度包检测)标记数据包优先级。例如:为游戏启用端口转发(如UDP 3074-3078),为视频会议保留固定带宽(如50Mbps)。
| 应用场景 | 推荐优先级 | 带宽保障值 | 典型协议 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 在线游戏(如《英雄联盟》) | 高(QoS Level 1) | ≥30Mbps | UDP/TCP混合 |
| 4K视频流(如Netflix) | 中(QoS Level 2) | ≥25Mbps | RTP/RTSP |
| IoT设备通信(如智能灯泡) | 低(QoS Level 4) | ≥1Mbps | MQTT/CoAP |
八、Mesh组网与拓扑优化
分布式网络适配
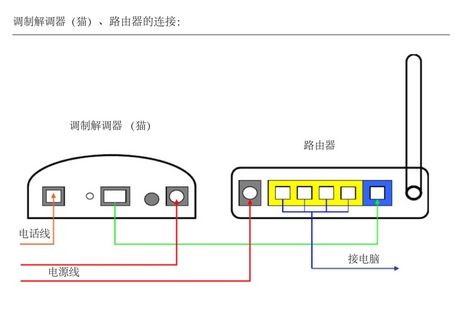
多节点路由器需支持自动拓扑规划,例如:通过回传链路质量选择主路由节点,动态调整子节点的信道和功率。支持有线回传(如LAN口聚合)可提升Mesh性能,避免无线回传的带宽衰减。
| 组网方式 | 带宽损耗率 | 部署难度 | 适用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 无线Mesh(单频) | ≥50%(2.4GHz) | 低(即插即用) | 小型公寓/临时覆盖 |
| 无线Mesh(双频) | ≤30%(5GHz回传) | 中(需手动选信道) | 大户型/复式住宅 |
| 有线回传Mesh | <10%(千兆LAN) | 高(需布线) | 企业/别墅全覆盖 |
路由器适配网络的核心逻辑是平衡性能与覆盖、兼容与安全、静态配置与动态优化。随着Wi-Fi 7、AI驱动网络等技术的普及,未来路由器将更注重智能化适配,例如通过机器学习预测用户行为、自动规避干扰频段、为VR/AR设备预留超低延迟通道。用户在选择路由器时,需优先关注硬件规格(如FEM数量、PA功率)、软件生态(如是否支持第三方固件)、扩展能力(如USB3.0接口/SDK开放度),并结合实际环境测试覆盖盲区和速率瓶颈。最终,适配网络的本质是为不同场景提供“恰到好处”的连接服务,而非盲目追求参数最大化。































































































































































































































发表评论